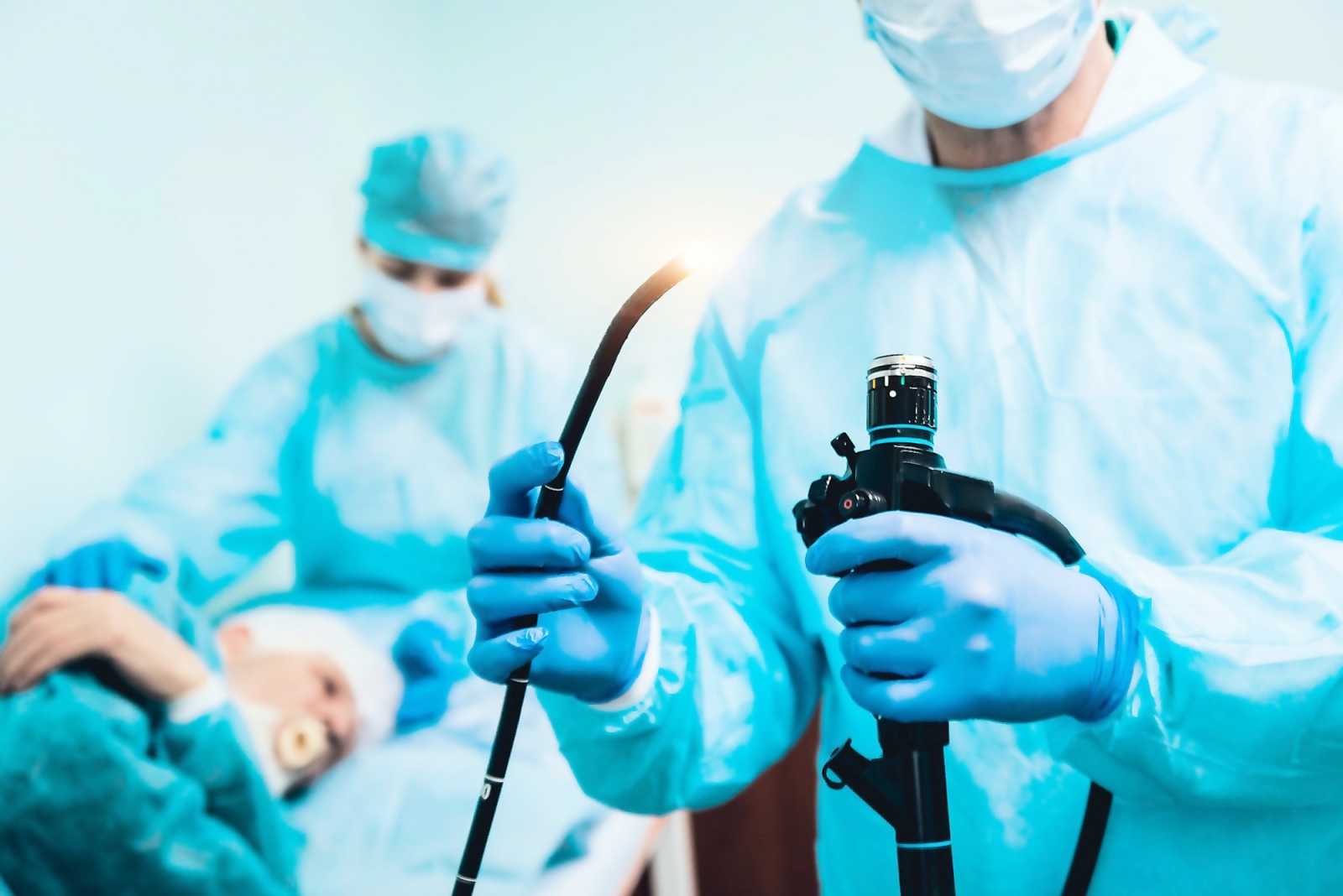
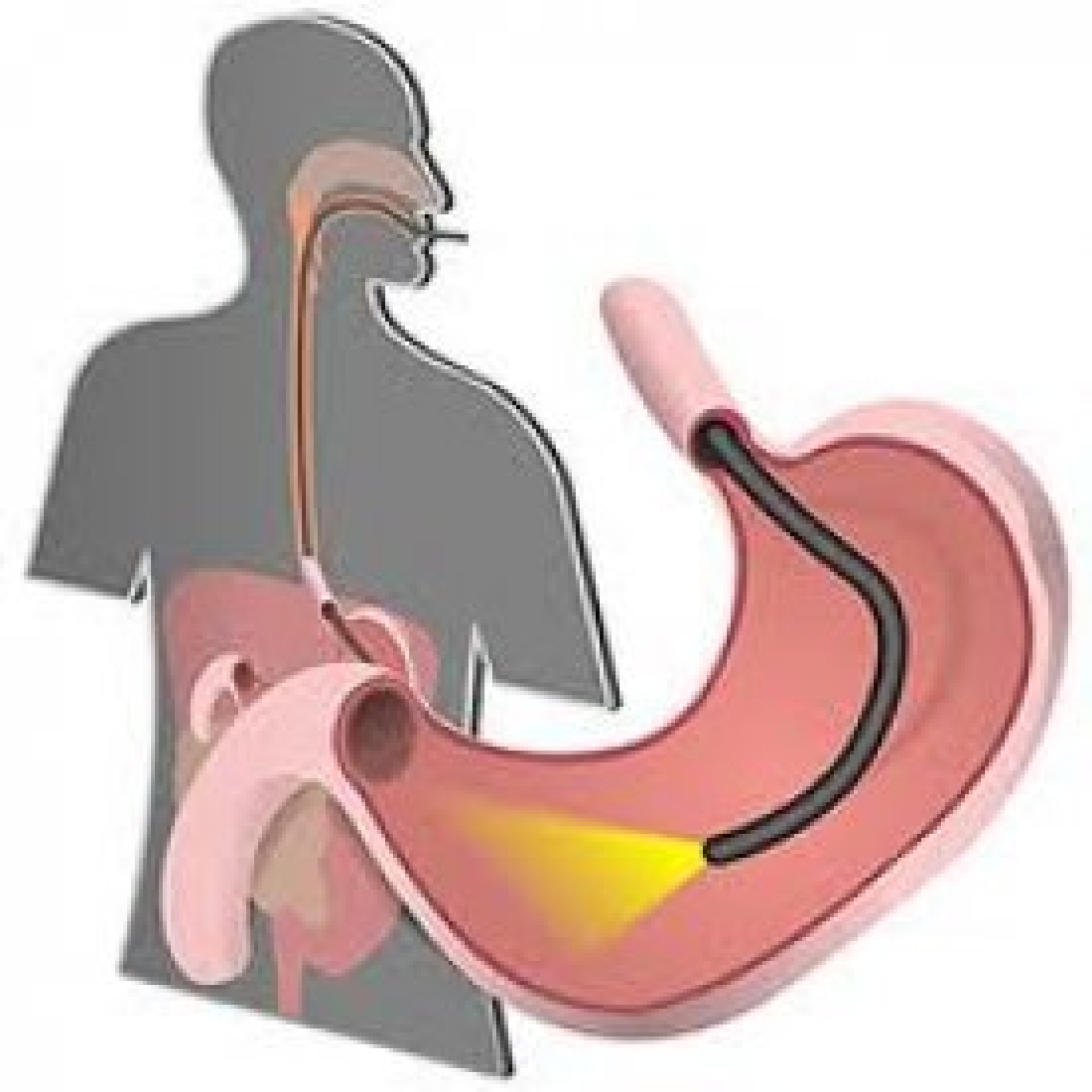
WHAT IS GASTROSCOPY?
It is a procedure that allows a doctor to look at the lining of the digestive system. The upper digestive tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum (the first part of the small intestine).
WHEN IS GASTROSCOPY PERFORMED?
Gastroscopy may be required if you have one of the following conditions:
• Unexplained pain in your upper abdomen
• If you have a condition called "acid reflux"
• If you have long-standing nausea and vomiting
• If you have long-term diarrhea
• If you have bloody vomit or black stools
• Difficulty swallowing or feeling stuck in your throat
• If you have abnormal results on other tests of your digestive system
• When objects that should not be swallowed are swallowed
• If you have some ulcers or lesions in your digestive system that your doctor wants to monitor
WHAT SHOULD I DO BEFORE GASTROSCOPY? 6-8 hours of fasting is sufficient before the endoscopy procedure. Consult your endoscopy doctor about whether some of the medications you are using (such as blood thinners) should be discontinued before the procedure. HOW IS
GASTROSCOPY PERFORMED?
An intravenous line is opened and medications are given to relax you and help you sleep. After a plastic mouthpiece is placed in your mouth, your doctor inserts a thin tube with a camera and light at the end into your mouth and examines your esophagus, stomach and duodenum, respectively. Your doctor examines these areas for irritation, bleeding, ulcers, or some lesions that tend to grow. During gastroscopy, your doctor may also do the following:
• Taking a biopsy: During a biopsy, your doctor takes a small piece of tissue from the lining of your digestive system. This piece is then examined under a microscope in the pathology laboratory.
• Some problems can be treated: For example, bleeding can be stopped. Some lesions that tend to grow (such as polyps) can be removed. A narrow area anywhere in the esophagus can be widened (with a balloon or stent).
WHAT HAPPENS AFTER GASTROSCOPY?
After gastroscopy, you will be monitored for 1-2 hours until the effects of the medications wear off. Most physicians recommend not driving or doing tasks that require attention after endoscopy. You can drive or return to work the next day.
WHAT ARE THE SIDE EFFECTS OF GASTROSCOPY?
The most common side effect is bloating. Some people may experience nausea due to the medications used before the procedure. If this happens to you, your doctor can prescribe medications that can reduce it. Most people can eat as usual after the procedure, after enough time has passed.
EXTREMELY RARE SIDE EFFECTS:
• Swelling and redness around the vascular access
• Food residues in the stomach escape into the lungs
• Bleeding, for example after a polypectomy
• Perforation in the digestive tract
IF ANY OF THE FOLLOWING EXPERIENCES, CALL YOUR DOCTOR OR NURSE:
• Abdominal pain that is much worse than gas or cramps
• A swollen and hard abdomen
• Vomiting
• Fire
• Difficulty swallowing or severe sore throat
• Black colored stools
• "Crackling" sensation under the skin in the neck area






 info@osmanogluhastanesi.com.tr
info@osmanogluhastanesi.com.tr +90 850 800 50 50
+90 850 800 50 50 WhatsApp
WhatsApp